Curation
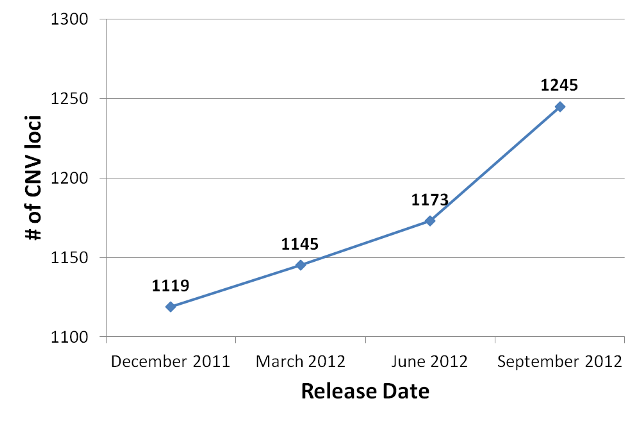
As with the other modules of AutDB, the content of the CNV module originates entirely from published scientific literature. MindSpec researchers systematically search, collect and extract information on CNVs from autistic case cohorts and, when available, unaffected control cohorts. CNVs in the module are organized based upon the locus (chromosomal region or band) in which they were observed in each annotated report.
CNV reports generally fall into three broad categories:
(1) Case studies. Case studies typically involve one or, at most, a few autistic individuals in which one or more potentially relevant CNVs has been identified. Case studies frequently have very detailed information on the clinical history and profile of the individual(s) in the report.
(2) Studies focused on one particular CNV locus. A number of reports deal with either identifying the frequency of CNVs at a particular locus across a given autistic population, or with describing the range of phentoypes within a group of autistic individuals with CNVs at a specific locus.
(3) Large-scale, genome-wide CNV screens. In this type of report, large autistic populations are screened across their genomes for CNVs. While such reports typically do not have a great deal of detail with regards to the clinical histories of individuals with case cohorts, they are critical for determining the frequencies and prevalence of potentially pathogenic CNVs across the genome.
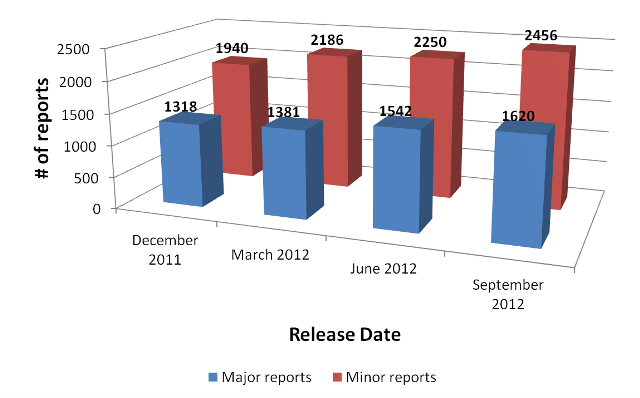
For any given CNV locus, a published report can be characterized as either major or minor. If the report class for a CNV locus in a published report is described as major, that means that an independent secondary methodology was used to confirm or validate at least one copy number variant within the locus of interest following its initial discovery. On the other hand, if the report class for a CNV locus is listed as minor, no subsequent validation or confirmation step was performed following the initial discovery of any CNV at the locus of interest.
In addition, additional information for every CNV locus is provided in the form of external links on their corresponding CNV summary page to two genome browsers, the UCSC Genome Browser and the NCBI Genome Browser. Both genome browsers provide valuable information on the genetic composition on each CNV in the module. Furthermore, if a CNV locus in the module is associated with one or more genetic disorders or syndromes in the DECIPHER database, an external link (or links) is provided to the corresponding syndrome(s) on the DECIPHER wesbite (http://decipher.sanger.ac.uk/). If there is no corresponding syndrome or genetic disorders in the DECIPHER database, no external link to DECIPHER is provided.